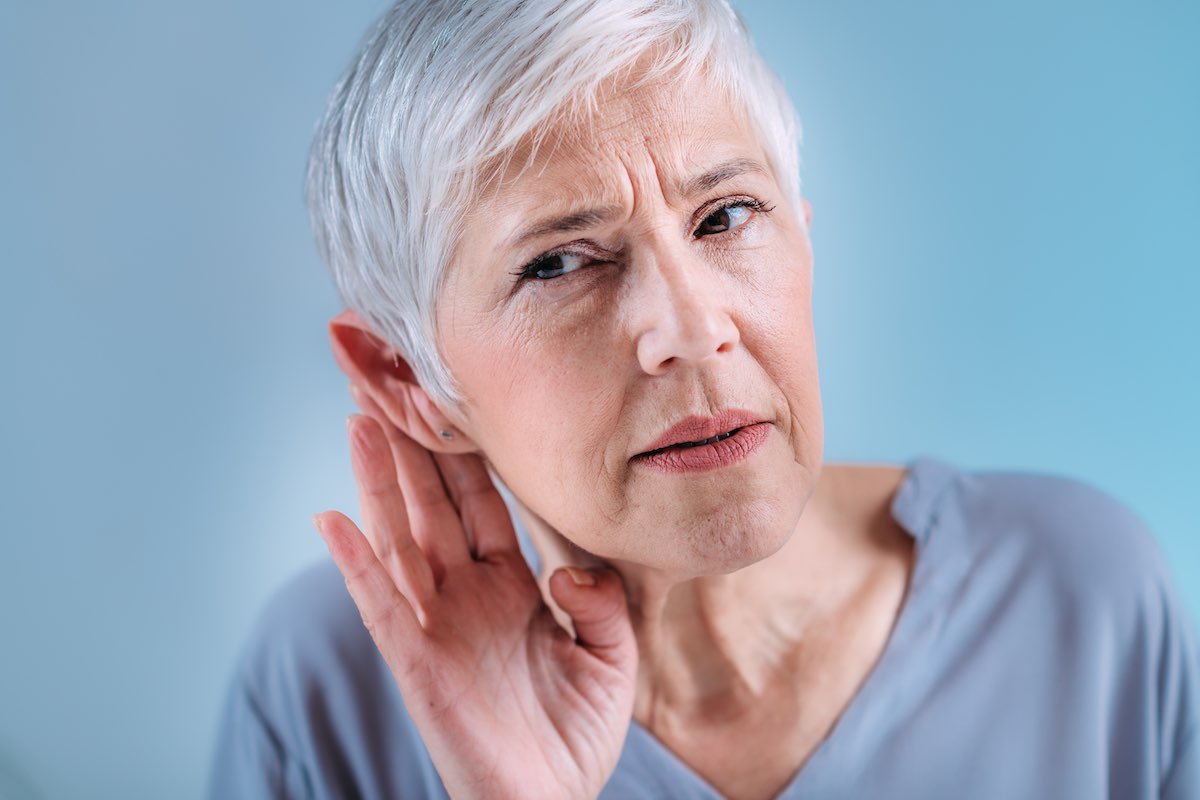
If you’re finding it harder to follow conversations or hear the TV, you’re not alone. Hearing loss that occurs gradually in older adults is a common condition called presbycusis. Anyone of any age can have hearing loss in one or both ears that ranges from mild to profound. In older adults, age-related hearing loss is common and can have troubling effects.
Struggling to hear can lead to increased risk of falls, depression, social isolation, and poor quality of life. According to Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, people with hearing loss over a period of 10 years have a 47% increased rate of hospitalization. The Lancet International Commission on Dementia, Prevention, Intervention, and Care has estimated that treating and eliminating midlife hearing loss can reduce the risk of dementia by 9%.
According to the World Health Organization, an individual who has hearing loss can’t hear as well as someone with normal hearing, which means a hearing loss threshold of 20 decibels or more in both ears. An example of a 20-decibel sound is someone whispering from 5 feet away. To test for hearing loss, an individual is played tones at different frequencies, typically between 125–8,000 hertz.
If you’re finding yourself asking people to repeat what they’ve said far too often, read on to learn what you can do to prevent and treat hearing loss.
What Are the Symptoms of Hearing Loss?

Age-related hearing loss comes on gradually and may be imperceptible at first. If you have hearing loss, you may find yourself turning up the volume on your phone, computer, or television often. You may also realize you’re asking people to repeat themselves or are leaving social situations because you can’t follow conversations easily. Typically, friends and family are the first to notice these signs.
Over time, you may find yourself experiencing the following symptoms:
- Having trouble hearing higher-pitched sounds, such as birds chirping or children speaking
- Sounds seeming muffled
- Having trouble making out words
- Experiencing difficulty hearing nearby speech when you’re in a noisy environment, such as a crowded room
- Having trouble hearing consonants, such as S, T, or Z
What Are the Causes of Hearing Loss?
There are many potential causes of hearing loss. Some causes, such as wax buildup, can cause temporary hearing loss. Most hearing loss is permanent, but it can be treated with devices such as hearing aids.
Common hearing loss causes include:
- Ear infections
- Chronic sinus issues
- Acute noise exposure such as gunshots or explosions
- Presbycusis (changes in the inner ear caused by aging)
- Repeated or consistent exposure to loud noise
- Family history of hearing loss (genetics)
- Medical conditions such as diabetes
- Meniere’s disease (disruption of fluid balance in the inner ear)
- Autoimmune inner ear disease
- Medications (over 200 medications are ototoxic, which means they can cause hearing loss). These medications include chemotherapy drugs, certain antibiotics, and Viagra.
- Viral infection
- Stroke
- Earwax buildup (causes temporary hearing loss)
- Abnormal tumor of the hearing nerve (acoustic neuroma)
- Abnormal bone growth in the outer or middle ear
- Ruptured eardrum (this can be caused by pressure changes, intense blasts of noise, infection or a foreign object in the ear)
Difference Between Loud Noises of Common Sounds
Decades ago, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) determined that 70 decibels is the safe noise level threshold. Consistent or prolonged exposure to sounds over 70 decibels may cause hearing loss over time. The louder the noise is, the faster permanent hearing loss may occur.
Here are some examples of decibel sound levels: