Best Over-the-Counter Hearing Aids on the Market
Best Over-the-Counter Hearing Aids on the Ma...
Over-the-counter hearing aids may sound like a poor quality alternative to prescription hearing aids, and until somewhat recently that was the case. Over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids now contain much of the technology found in prescription-only hearing aids at significantly less cost to users. This means that older adults with mild to moderate hearing impairment can now purchase medical-grade hearing aids without visiting an audiologist.
There are many reasons why people avoid or delay treatment for hearing loss, but among them are certainly cost and convenience. In a recent survey of 1,000 hearing aid users, AgingInPlace.org found that 52.9% of respondents named cost as their biggest hesitation in purchasing. The FDA’s new ruling establishing regulations for the sale of medical grade OTC hearing aids provides greater access to the hearing impaired by cutting cost and the need for a hearing professional’s prescription.
Since hearing treatment is a vital part of aging in place for many older adults, we’ve researched the best over-the-counter hearing aids available to bring you our list of favorites.
Top Over-the-Counter Hearing Aids
AgingInPlace.org researched twelve popular brands to find the best OTC hearing aid devices. Here are six of the best, according to our editors:
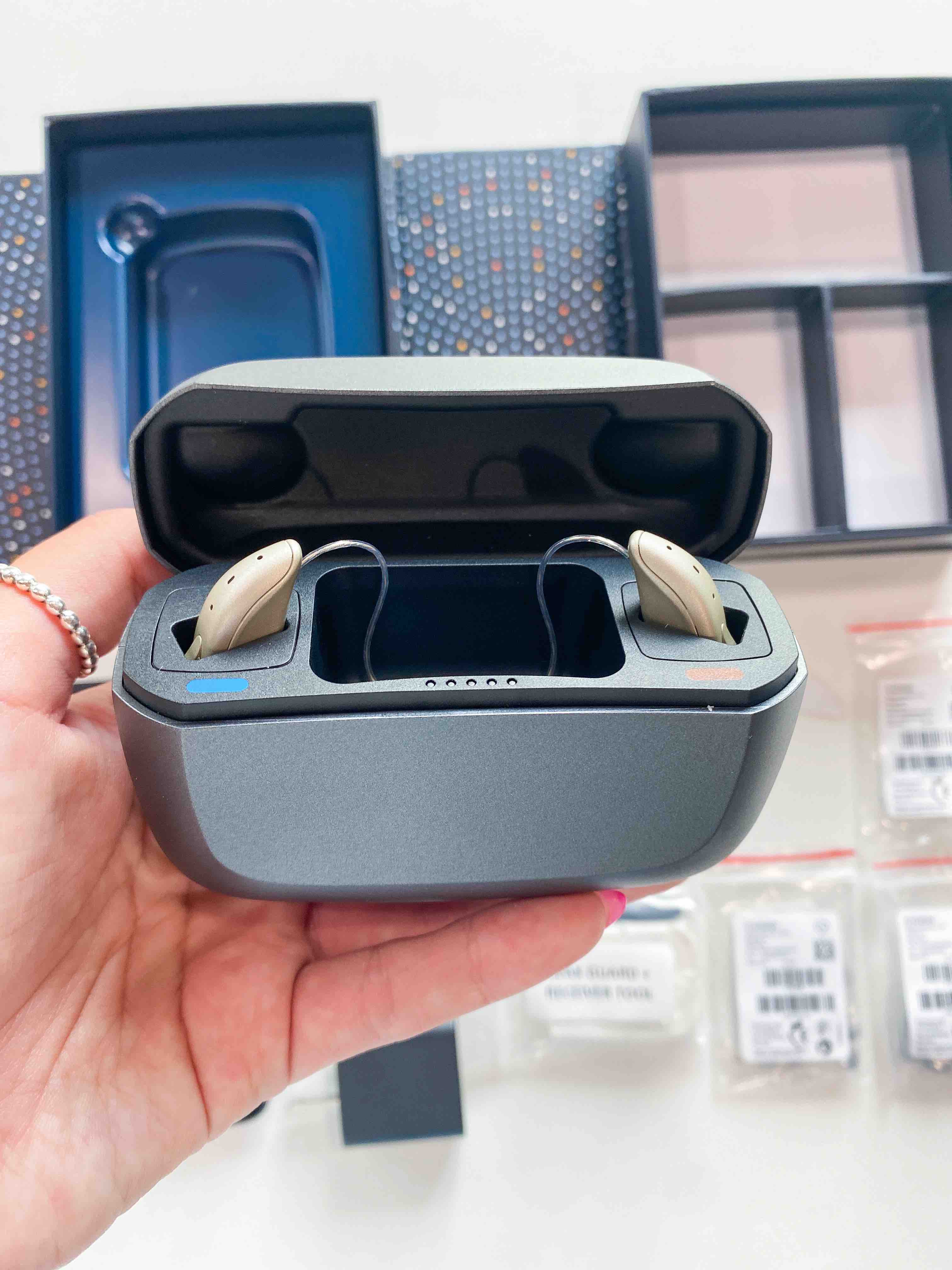
- Jabra Enhance Select 50 – Best Value
- Audien Atom – Best Protection Plan
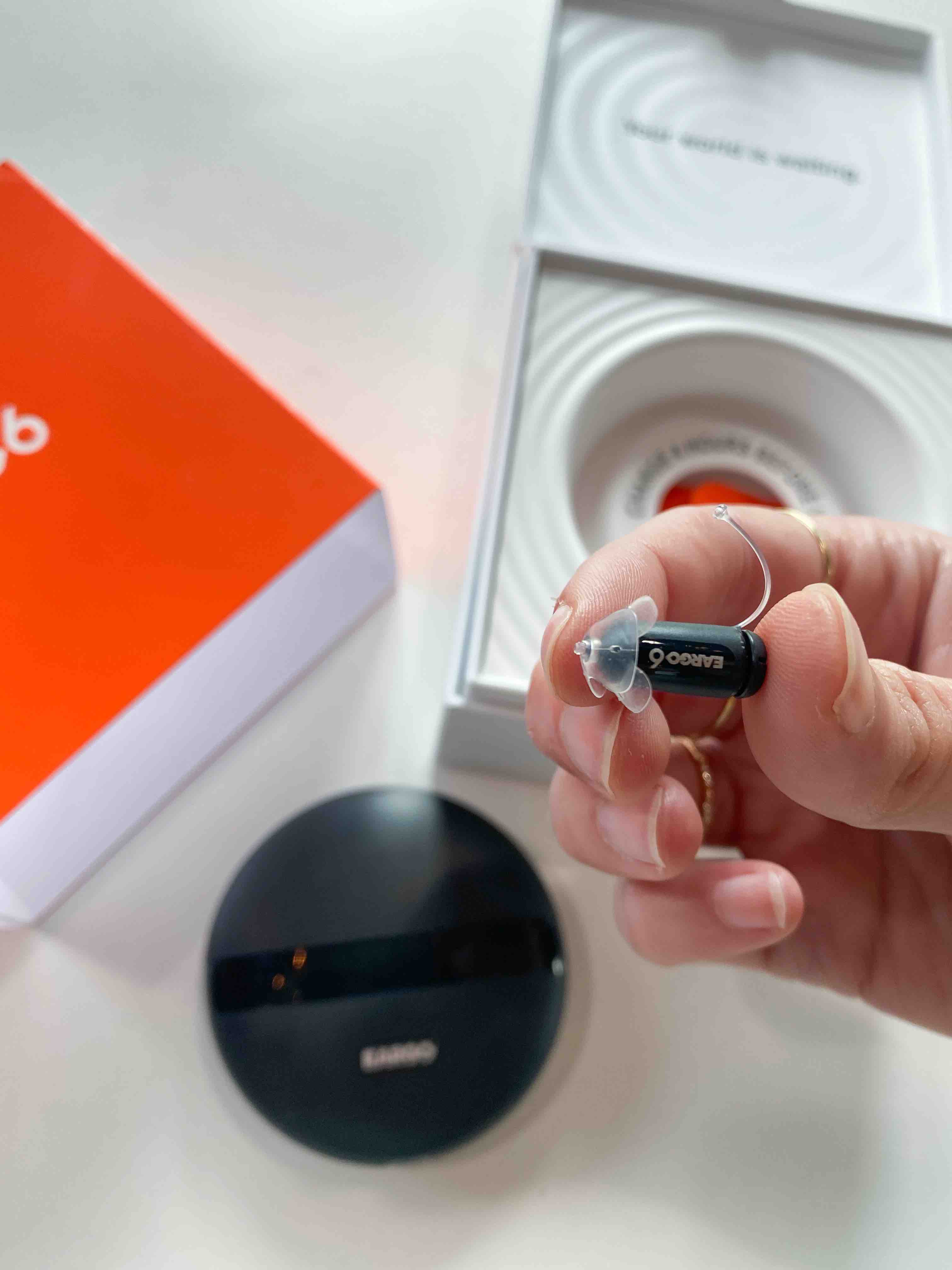
- Eargo 6 – Most Discreet
- MDHearing VOLT+ Best Basic
- Lexie B2 – Best Budget
- Audicus Omni – Most Advantaged Technology
How We Picked Our Favorite Over-the-Counter Hearing Aids
At AgingInPlace.org, we take our recommendations seriously. When it comes to medical-grade devices, we believe thorough testing and research is the best way to help our readers make the most informed decisions. We recently conducted a Hearing Aid Research and Testing Summit, giving us hands-on experience with various over-the-counter models and face time with both a focus group of hearing aid users and renowned experts in the field of audiology.
To create our list of the best over-the-counter hearing aids, we determined our top picks based on the following criteria:
- Price
- Audiologist care
- Warranty
- Customer service
- Features such as Bluetooth capability and rechargeable batteries
- Comfort and fit
- Reliability
Apart from our research and testing summit, our writers and editors have spent collectively more than 5,000 hours conducting in-depth research on hearing aids. Recent research regarding over-the-counter models have delved into product quality, accessibility, and subjective reviews. Throughout this process, we did the following:
- Engaged in ongoing independent research
- Consulted with independent audiologists
- Consulted with geriatric care experts
- Mystery shopped the brands
- Surveyed hundreds of hearing aid users
- Tested various models of hearing aids
- Interviewed experts in the field
- Read thousands of verified customer reviews from trusted third parties such as Better Business Bureau and Trustpilot
See our full Hearing Aids Ratings Methodology.
What Are Over-the-Counter Hearing Aids?
OTC hearing aids are FDA-regulated devices that address perceived mild to moderate hearing loss in adults age 18 and older. They can be purchased without a prescription or a visit to an audiologist.
A Brief History of OTC Hearing Aids
Congressional Mandate: A 2017 law mandated that the FDA create an over-the-counter (OTC) category of hearing aids for mild to moderate hearing loss. The move was intended to make it easier for the average consumer to access hearing aid technology—and make it more affordable.
Biden Executive Order: In July 2021, President Biden signed an executive order requiring the FDA to publish a proposed ruling on OTC hearing aids within 120 days.
FDA Final Regulations: In August 2022, the FDA finalized regulations for OTC hearing aids that allows brands to market and sell medical-grade devices directly to you—without the need for expensive visits to an audiologist.
The FDA ruling not only makes shopping for hearing aids easier by improving access, but it also put in place regulations that protect consumers from using potentially unsafe devices. Without access to regulated OTC hearing aids, many people may end up purchasing PSAPs (personal sound amplification products).
Regulation by the FDA means that OTC hearing aids have to conform to safety standards, while ensuring what is advertised is actually what you’re getting. The new regulations went into effect on October 17, 2022, and companies have until April 14, 2023 to achieve full compliance.
OTC Hearing Aids vs PSAPs
PSAPs can be inexpensive tools to increase volume. They don’t require FDA regulation and can be sold to all ages. PSAPs may seem like a simple solution, however hearing loss is more complex than just volume loss and includes considerations like pitch, tone, background noise, and even the direction sound is coming from. OTC hearing aids, as opposed to PSAPs, use various technologies that consider sound nuances like pitch, sound direction, volume, and different sound environments by providing much more detailed customization. Because they are more complex, they require FDA regulation and can only be sold to those aged 18 and older. If you have moderate-to-severe hearing loss, then you require the attention of an audiologist.
Best Over-the-Counter Hearing Aids
- Cost: $1,195 per pair for Enhance Select 50
- Type of hearing aid: Receiver-in-canal (RIC)
- Type of hearing loss: Mild to moderate
- Bluetooth capabilities: ✅
- Telecoil: ❌
- Warranty/trial period: 100-day risk-free trial and three-year warranty
- Financing: ✅
Pros
-
Three years of follow-up care
-
Adjustments with audiologists via Jabra Enhance Select’s app
Cons
-
Requires smartphone or tablet
-
Doesn’t serve severe or profound hearing loss
-
No rechargeable option
-
No telecoil
Editor’s Choice
What Is Editor’s Choice?
Our team of editors and writers choose a product from each article that stands out based on our extensive research of the products we review. While it may not always be the highest-scoring product in the lineup, we’ve chosen the product based on its overall value to our audience.
Why We Chose This Product:
Jabra Enhance continues to impress us with their quality and service, and our hands-on testing with their products confirms the claims made by the company regarding ease of use and best-in-class audiology support.

- Cost: $99 per pair
- Type of hearing aid: In-the-canal (ITC)
- Type of hearing loss: Mild to moderate
- Bluetooth capabilities: ❌
- Rechargeable battery
- Telecoil: ❌
- Warranty/trial period: One-year warranty, 45-day money-back guarantee, lifetime protection for $4 per month
- Financing: ❌
Pros
-
Affordable
-
Small, discreet design
-
Wireless charging
Cons
-
No customization
-
No Bluetooth
-
No directional microphone
-
No noise reduction
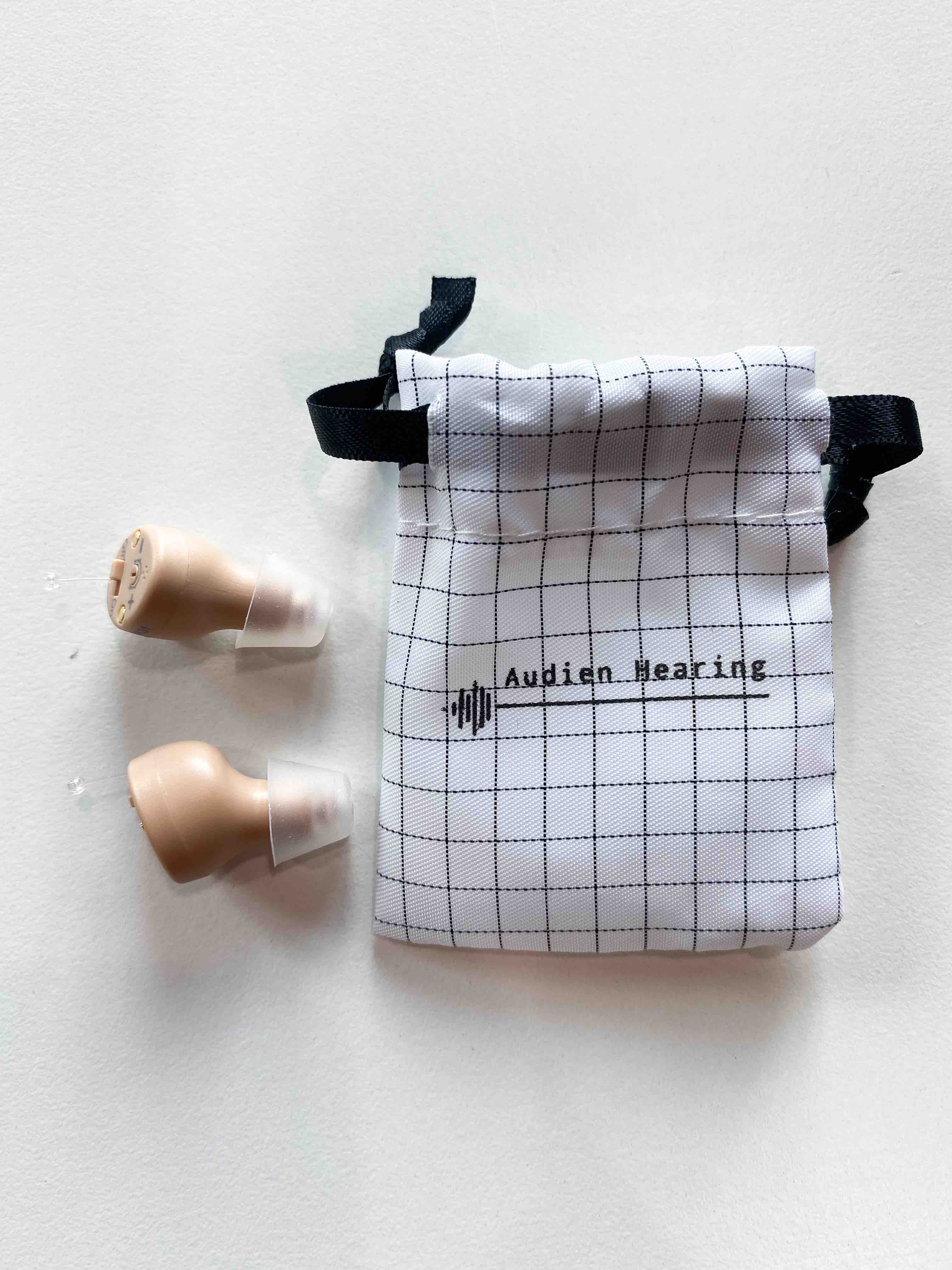

Note: Audien is not an FDA approved device, but it is FDA registered. This means that the FDA recognizes the manufacturing facility as an established entity, but it has not yet given Audien an approval.
- Cost: $2,450 per pair
- Type of hearing aid: Completely-in-the-canal (CIC)
- Type of hearing loss: Mild to moderate
- Bluetooth capabilities: ✅
- Rechargeable battery
- Telecoil: ❌
- Warranty/trial period: Two-year warranty and a 45-day trial period
- Financing: ✅
Pros
-
Free hearing aid test
-
Military members and veterans get significant discount
-
Nearly invisible design
-
IPX7 water resistant
Cons
-
No Bluetooth streaming
-
Dome shape needs lots of cleaning

- Cost: $1,199.99 per pair
- Type of hearing aid: Slim Tube Behind-the-ear (BTE)
- Type of hearing loss: Mild to moderate
- Bluetooth capabilities: ❌
- Rechargeable battery
- Telecoil: ❌
- Warranty/trial period: 90-day warranty and 45-day risk-free trial
- Financing: ✅
Pros
-
On-staff audiologist
-
Free shipping and 0% financing
Cons
-
No customization or adjustments available
-
One-size-fits-most
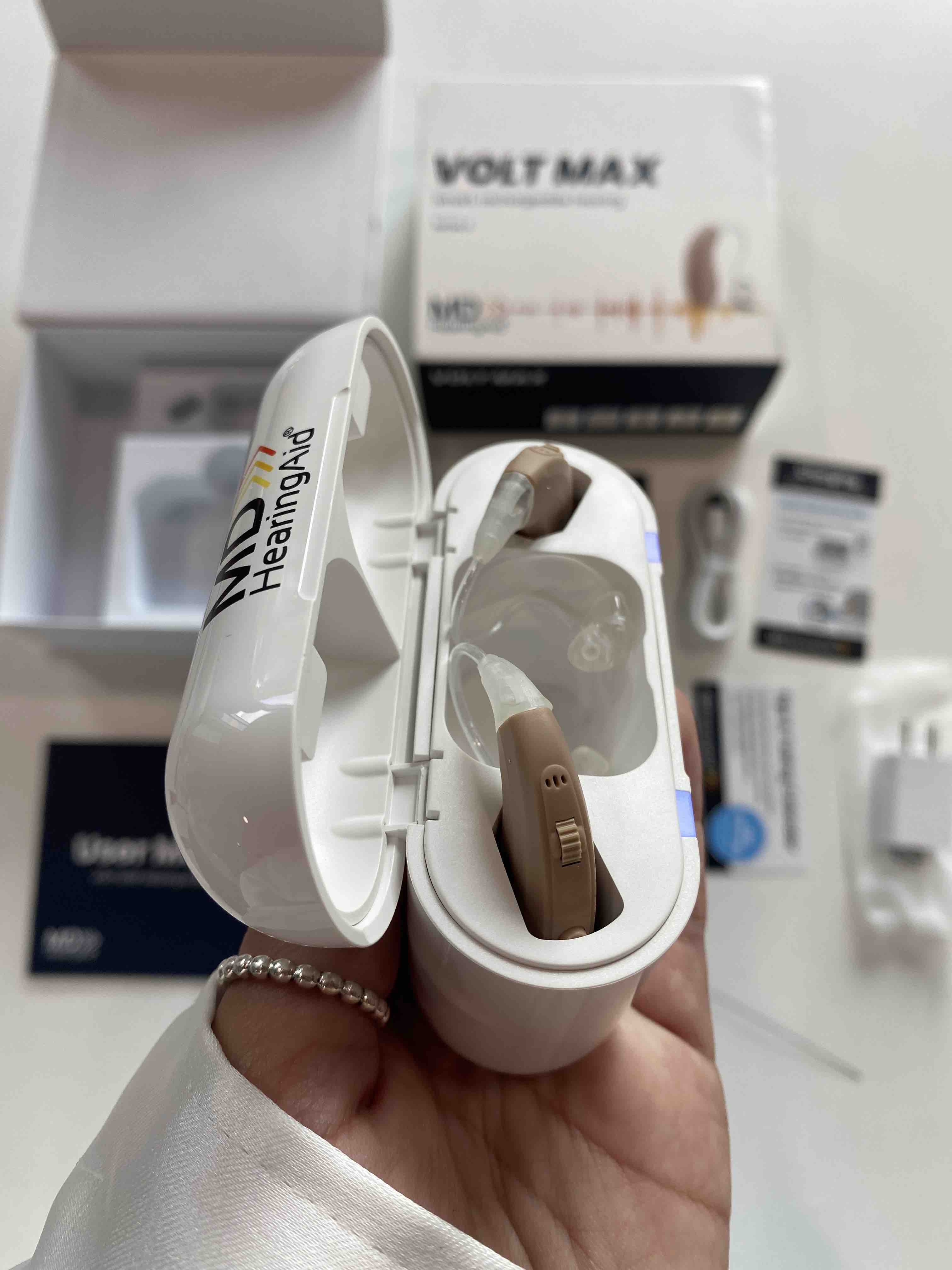
- Cost: $999 per pair upfront or $49 per month for a subscription
- Type of hearing aid: Slim Tube Behind-the-Ear (BTE)
- Type of hearing loss: Mild to moderate
- Bluetooth capabilities: ✅
- Rechargeable battery
- Telecoil: ❌
- Warranty/trial period: One-year manufacturer’s warranty, 45-day trial
- Financing: No, but there is a subscription option for those who can’t afford to pay upfront
Pros
-
Easy-to-use smartphone app
-
More affordable compared to other hearing aids
Cons
-
No 24/7 customer support
Note: We understand that many people’s finances are not flexible, and even with the payment plan option the Lexie B2 may be out of budget. We chose this model as our “Best for a Budget” pick due to the quality and technology it offers at less than half the cost of many other comparable models. If you’re looking for a truly inexpensive (though far less advanced) option, the Audien Atom is the least expensive choice on our list.
- Cost: $2,998 per pair (monthly payment pricing available at $159 per month)
- Type of hearing aid: Receiver-in-canal (RIC)
- Type of hearing loss: Mild to moderate
- Bluetooth capabilities: ✅ (Bluetooth streaming)
- Rechargeable battery option available
- Telecoil: ✅ (must request)
- Warranty/trial period: Two-year warranty and 45-day trial period
- Financing: ✅
Pros
-
Great ratings by consumers
-
Easy buying with membership available
-
Allows hands-free calling and music streaming from your smartphone
Cons
-
Accessories not covered in warranty
-
Repairs could take a while

Compare OTC Hearing Aids
| JABRA ENHANCE SELECT 50 | COST PER PAIR | $1,195 | TYPE OF HEARING AID | RIC | TYPE OF HEARING LOSS | Mild to moderate | BLUETOOTH | BATTERY | Disposable | TELECOIL | WARRANTY | 3 years | TRIAL PERIOD | 100 days | FINANCING |
|---|
| AUDIEN ATOM | COST PER PAIR | $99 | TYPE OF HEARING AID | ITC | TYPE OF HEARING LOSS | Mild to moderate | BLUETOOTH | BATTERY | Rechargeable | TELECOIL | WARRANTY | 1 year | TRIAL PERIOD | 45 Days | FINANCING |
|---|
| EARGO 6 | COST PER PAIR | $2,450 | TYPE OF HEARING AID | CIC | TYPE OF HEARING LOSS | Mild to moderate | BLUETOOTH | BATTERY | Rechargeable | TELECOIL | WARRANTY | 2 year | TRIAL PERIOD | 45 Days | FINANCING |
|---|
| MDHEARING VOLT+ | COST PER PAIR | $1,199.99 | TYPE OF HEARING AID | BTE | TYPE OF HEARING LOSS | Mild to moderate | BLUETOOTH | BATTERY | Rechargeable | TELECOIL | WARRANTY | 90 days | TRIAL PERIOD | 45 Days | FINANCING |
|---|
| LEXIE B2 | COST PER PAIR | $999 or $49/month for a subscription | TYPE OF HEARING AID | BTE | TYPE OF HEARING LOSS | Mild to moderate | BLUETOOTH | BATTERY | Rechargeable | TELECOIL | WARRANTY | 1 year | TRIAL PERIOD | 45 Days | FINANCING |
|---|
| AUDICUS OMNI | COST PER PAIR | $3,398 or $159 per month for a membership | TYPE OF HEARING AID | RIC | TYPE OF HEARING LOSS | Mild to moderate | BLUETOOTH | Streaming available | BATTERY | Rechargeable | TELECOIL | WARRANTY | 1 year | TRIAL PERIOD | 45 Days | FINANCING |
|---|
Cost of Over-the-Counter Hearing Aids
OTC hearing aid prices vary significantly, but you can expect to pay anywhere between $100–$3,000 for a single hearing aid. In contrast, prescription hearing aids pricing can be anywhere between $1,500–$6,000. While prescription hearing aids often contain more advanced technology or fitting features, functionality isn’t much different than current OTC hearing aids. OTC models are able to be sold at a much lower price point because they aren’t also helping cover overhead costs like office expenses and salaries of audiology office staff.
OTC hearing aids sold directly to consumers are often eligible for financing through the manufacturer or through third-party financing companies partnered with the manufacturer (audiologists or dispensers also often offer third-party financing). Financing may be offered in terms of up to 36 months or more, often with no interest for eligible buyers. Companies like Lexie and Audicus offer unique subscription plans that are similar to financing, where the cost of your hearing aids is broken down into monthly payments and combined with other perks and features to result in a monthly membership fee with a set commitment term.
How Can I Save Money on Over-the-Counter Hearing Aids?
In addition to the already lower cost of OTC hearing aids, there are other ways you may be able to save money on your purchase. Most insurance policies don’t cover hearing aids, but it can’t hurt to contact your insurance company directly as some policies may offer limited or situational coverage. Hearing aids can be eligible purchases under health savings accounts or flexible spending accounts, which allow you to use untaxed money for qualifying purchases. If you know you need two hearing aids, some models offer discounts for buying two instead of one. Lastly, many OTC hearing aid companies run deals and promotions, often resulting in significant savings.
Pros and Cons of Over-the-Counter Hearing Aids
Purchasing OTC hearing aids may seem like an excellent alternative to the traditional method of going through an audiologist, but OTC hearing aids aren’t the best option for everyone. Depending on your needs, complexity of hearing loss, and overall health history, OTC hearing aids have advantages and disadvantages.
Pros
-
They’re less expensive. For the most part, OTC hearing aids are less costly than prescription ones.
-
They’re convenient. When you buy OTC hearing aids, you’re able to skip the visit to the audiologist, which is great if you’re busy and pressed for time.
-
They’re effective. Many OTC hearing aids work just as well as prescription models.
Cons
-
OTC hearing aids offer fewer options for customization. Because an audiologist won’t fine-tune the settings for your OTC hearing aid, it may not be able to meet all your needs.
-
You don’t get the benefit of real ear measurement (REM). This is when an audiologist or dispenser measures the output of the hearing aid at different frequencies to ensure the prescription is being met. “Research shows that conducting REMs is the number one best practice one can do for positive patient outcomes,” said Dr. Faivre.
-
They’re not suitable for severe hearing loss. Most OTC devices won’t help people with severe forms of hearing loss.
-
Skipping an in-person exam isn’t always a good idea. Some forms of hearing loss have underlying causes that may require medical treatment that an OTC hearing device can’t provide.
-
The OTC hearing aid market is saturated. There are a lot of subpar devices out there misrepresenting themselves as medical-grade hearing aids, and consumers may not know how to tell the difference.
-
Many OTC hearing aids sacrifice high-tech Bluetooth streaming capabilities for affordability, but not all. If you want to stream music or take phone calls hands-free, you’ll need to budget for a hearing aid like the Jabra Enhance Select 200 model at $1,995 per pair.
Who Should Use Over-the-Counter Hearing Aids?
Research shows that the effects of impaired hearing impacts more people than we may have thought. In a study connecting hearing loss with healthy aging, researchers found: “Six of 10 people with moderate-to-severe hearing loss do not have hearing aids, and 70% of people between ages 65 and 84 do not use hearing aids.” This suggests that the implications of hearing loss extends far beyond communication. Hearing loss affects personal relationships, increases the chance of falls and other accidents, and has a negative impact on overall well-being.
According to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders, OTC hearing aids are suitable for adults with mild-to-moderate hearing loss. Many cases of hearing loss are complicated or exacerbated by other conditions, so it’s important to ensure your hearing loss doesn’t have an underlying cause before choosing an OTC hearing aid. Hearing loss is associated with comorbidities such as diabetes, heart disease, hypertension, high cholesterol, dementia, kidney disease, thyroid disease, and depression, noted Dr. Faivre.
Hearing loss combined with other symptoms like confusion, vertigo, or headaches may mean that you could have other conditions in need of treatment, or at least a more complex form of hearing loss that requires audiologist care.
You are likely a good candidate for OTC hearing aids if you:
- Are able to hear most of the time with some difficulty on occasion
- Your hearing loss is limited to low volumes or chaotic sounds where selective hearing is needed (like noisy public places)
- You have to ask people to repeat themselves during conversations, but can usually hear when things are repeated
- Your friends and family have expressed that they feel like you can’t hear as well as you used to
- You have no other physical symptoms or ailments
Online and In-Office Hearing Tests
If you’re unsure if you’re a good candidate for OTC hearing aids, you can take an online hearing test to screen yourself. However, it might be wise to get tested by a hearing professional for the most thorough results. Online hearing tests can help indicate whether you’re experiencing impairment, but they aren’t comprehensive and won’t be able to diagnose the cause of your hearing loss. Issues like wax buildup can reduce your hearing, but you could also have a more complex issue that warrants an audiologist consultation.
According to the Journal of the American Academy of Audiology, home hearing tests are accurate at establishing pure-tone air-conduction thresholds (presenting a pure tone to the ear through an earphone to measure sensitivity) and can be used to measure accurate air-conduction hearing thresholds (transmitting sound vibrations to the eardrum to identify obstruction or hearing loss in the outer, middle, and inner ear). They can help you determine whether you should pursue further testing, and taking them periodically can also let you know if your hearing loss is worsening.
These tests are easy to take and give you the means to evaluate your hearing from the comfort of your home, providing greater accessibility and a cost-effective option to test your hearing. If after taking an online test you find that you do in fact have hearing loss, you can schedule a visit with an audiologist for a full diagnostic test.
How to Find the Best-Fitting Over-the-Counter Hearing Aid
Fit is an important factor in selecting a hearing aid, and most OTC hearing aids will fit slightly differently. Besides fit, Shauna Hatcher, a member of the medical review board for the National Wellness and Public Health Network, said the warranty, trial period, and modification capability are the most important considerations when purchasing a hearing aid. Things to look for to find the best-fitting and most suitable OTC hearing aid include:
- Warranty: Look for products that come with at least a one-year warranty. Ideally, brands will also include loss, damage, and repair coverage with your purchase.
- Trial period: “Most manufacturers provide at least a 30-day trial period,” said Hatcher. However, she warns that some brands have nonrefundable fees that you may still have to pay even if you decide to return the device. Make the most of your trial period by using your hearing aid in as many situations as possible, like going to a movie, eating at a restaurant, or seeing live music if that’s something you do often.
- Modifications: Ask whether repairs and modifications are included in the price. “You may wind up paying more for a hearing aid that includes continuing care, but the peace of mind is frequently worth it,” said Hatcher.
- Fit: Unlike a custom-fitted prescription hearing aid, there’s likely to be some trial and error with an over-the-counter device. A hearing aid should fit snugly so it doesn’t move around, but it should ultimately be barely noticeable. To ensure you get the best fitting device, choose hearing aids that come with a free trial period. And if the fit isn’t right, you can return the devices for a full refund.
Bottom Line
With so many OTC hearing aid devices on the market today, shopping for one can be a confusing experience. But several brands offer high-quality non-prescription hearing aids that you can easily buy online. If you experience mild-to-moderate hearing loss and are comfortable purchasing a hearing aid without an audiologist consultation, there are plenty of affordable and low-risk options available to suit your needs.
Steph Coelho contributed to this report.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Yes. However, the FDA recommends getting a hearing test. Additionally, people under 18 years of age can’t buy a hearing aid without first getting a hearing test.
WRITTEN BY
With over six years of clinical experience in long term care and rehabilitation, Ayla is passionate about helping people age safely and with dignity. She is an LPN (Licensed Practical Nurse), licensed with the State Board of Nursing in Massachusetts, and holds a B.A. in Psychology. Through her education and work she has focused on combining practical health knowledge with the individual needs and desires of older adults to bring the absolute best care and content to patients and readers.
MEDICALLY REVIEWED BY
Dr. Magann Faivre is an audiologist with a passion for being active in audiology organizations, particularly concerning advocacy, patients’ rights issues, and teaching student leadership. She intimately grew up around hearing loss and empathizes with patients when discussing their hearing journey. She is dedicated to creating a positive and integrative hearing healthcare experience so patients leave informed and confident. Dr. Magann Faivre currently serves on The Audiology Project’s Board of Directors and on Northern Illinois University’s Advisory Board. She is a longstanding fellow of the American Academy of Audiology and Academy of Doctors of Audiology.